RNN/LSTM/GRU
RNN
RNN:Recurrent Neural Networks,循环神经网络,能够应用于空间或时间先后相关的场景,比如文字解析、语音识别。
RNN模型结构简单描述,如下图:
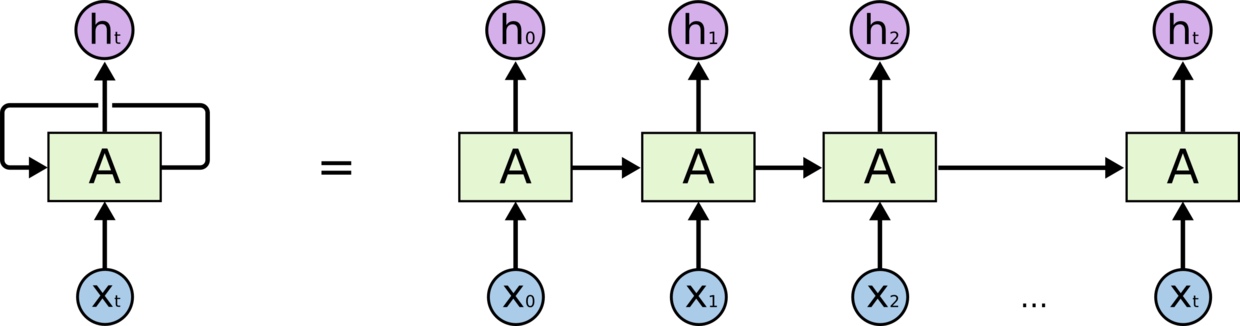
其中X0、X1、……、Xt,可以理解成多个输入,或者对单个输入拆分成的多个输入,比如一张图片的多个字符拆分、语音的拆分等等;h0、h1、…、ht可以理解成多个输出,通常也可能最终被concat到一起,做为一个输入。
上图是单向的,也就是h1会受h0的影响,h2会受h1、h0的影响,…,但反过来不会。RNN网络也会有双向的情况,使前后互相影响。
LSTM
LSTM:Long Short Term Memory,长短期记忆神经网络,RNN中的一类,用来避免长期依赖问题,被Alex Graves改良和推广。
LSTM模型结构简单描述,如下图:
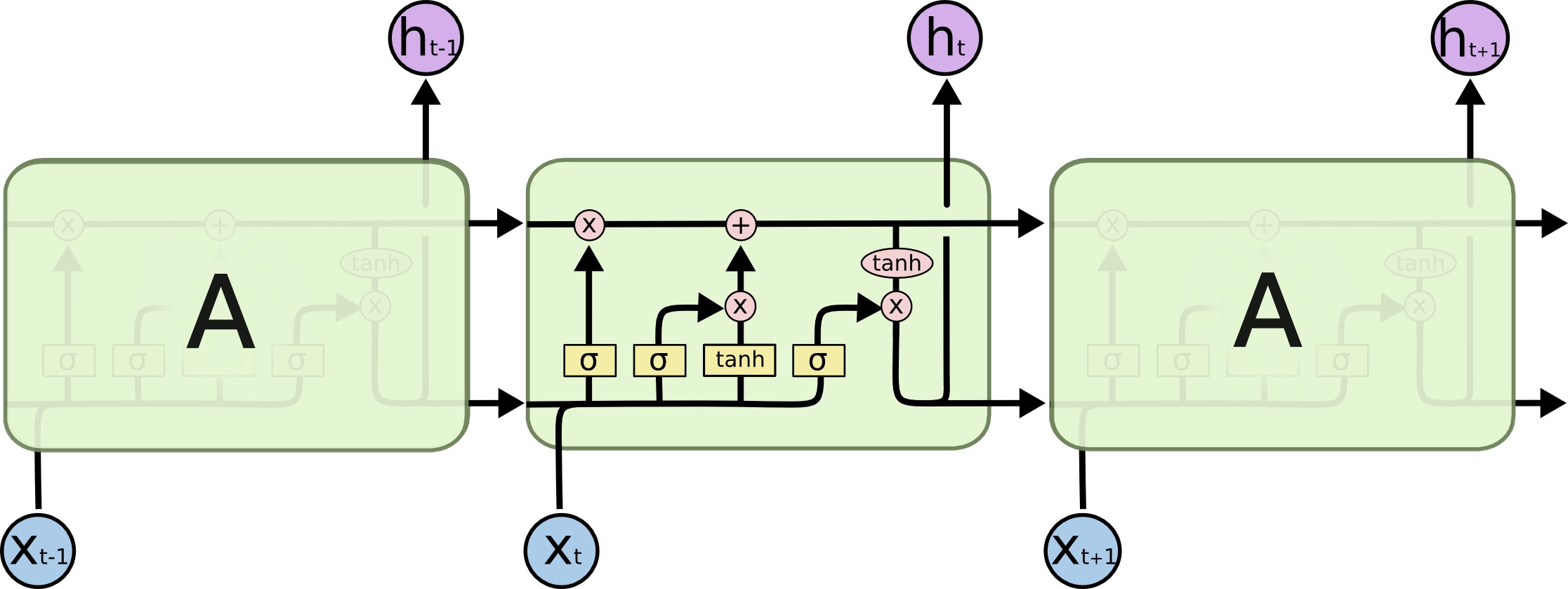
每个LSTM单元有两个状态传递:Ct (细胞状态) 和ht (隐藏状态)。通常Ct的更新比较慢,ht更新比较快。
LSTM可以拆分成4个步骤fico: forget gate、input gate、cell、output gate。
遗忘门 (forget gate)
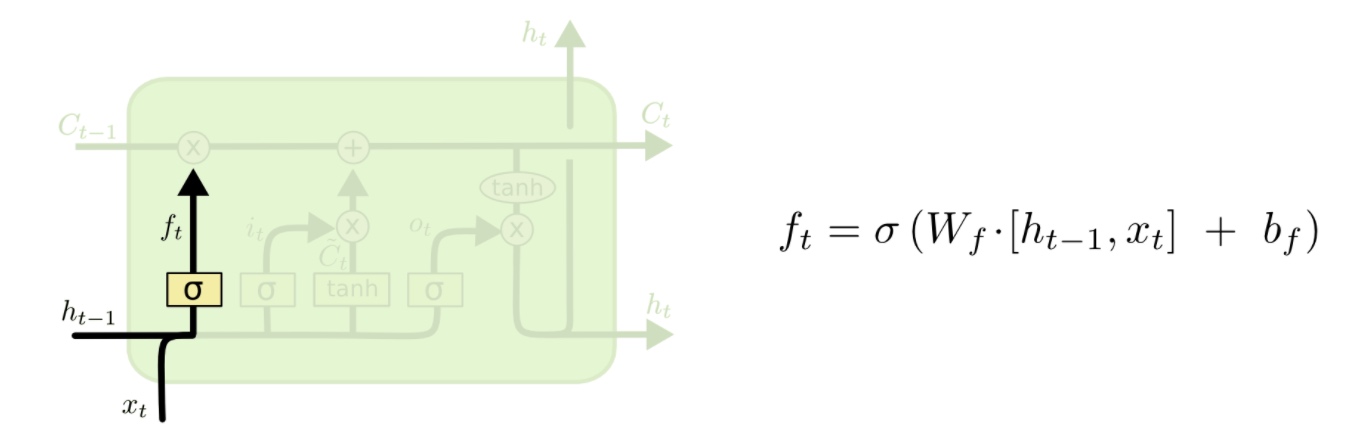
σ是sigmoid函数,产生0到1直接的数值,决定Ct-1更新多少,可以理解成丢弃多少,所以称作遗忘门。
实际应用中,C0和h0可以是全0向量(caffe),也可能是权重(onnx)。
输入门 (input gate)
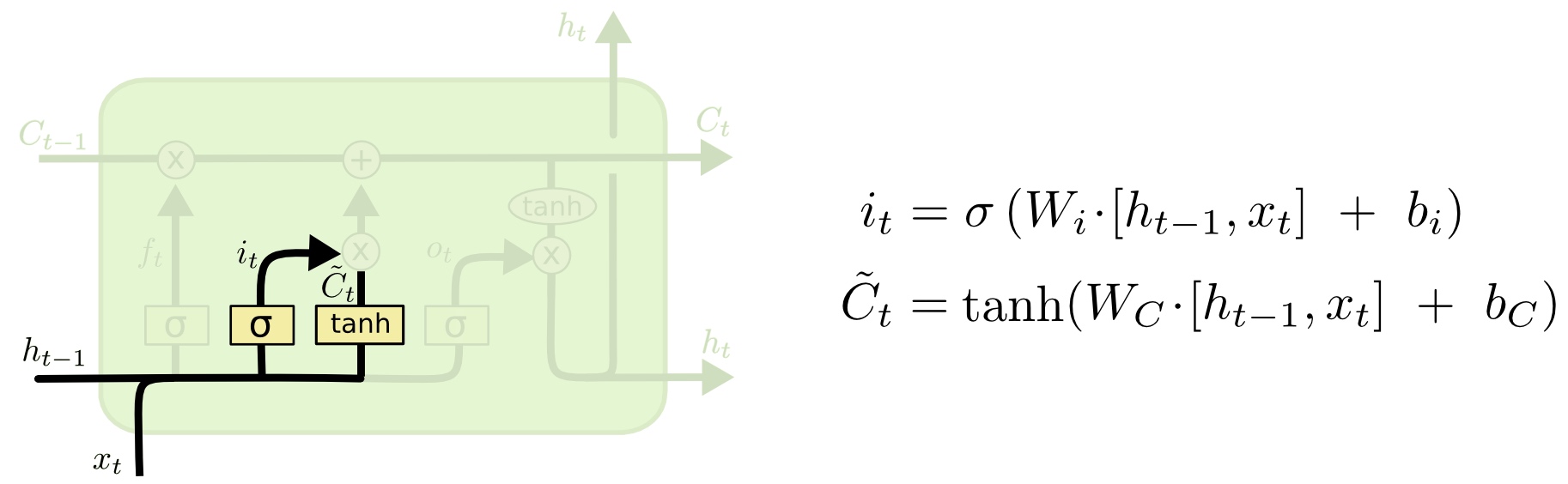
it也是由sigmoid函数更新,决定对输入更新多少; $ \widetilde{C}_{t} $由tanh函数实现,决定有多少数据会添加到细胞状态中。
细胞状态更新 (cell)
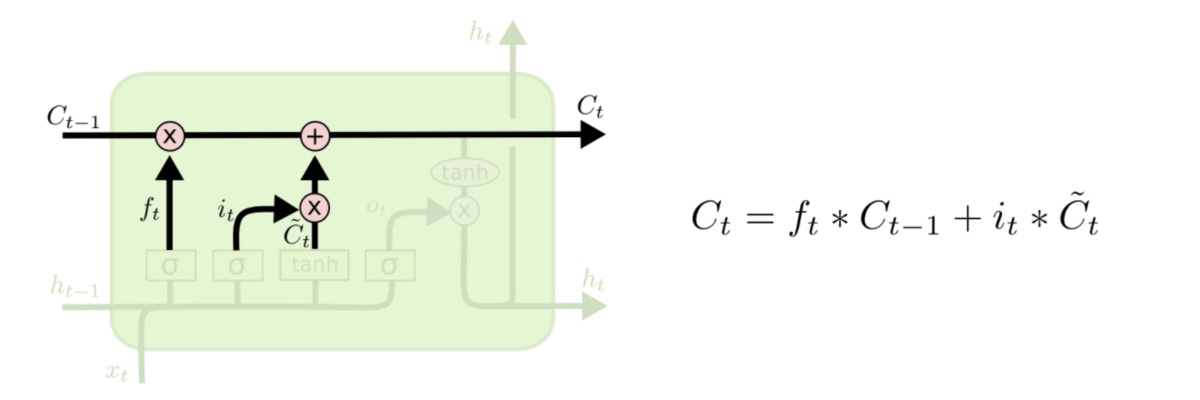
通过前面的遗忘门和输入门,对细胞状态更新Ct-1到Ct,作为一个单元的细胞状态输入。
输出门 (output gate)
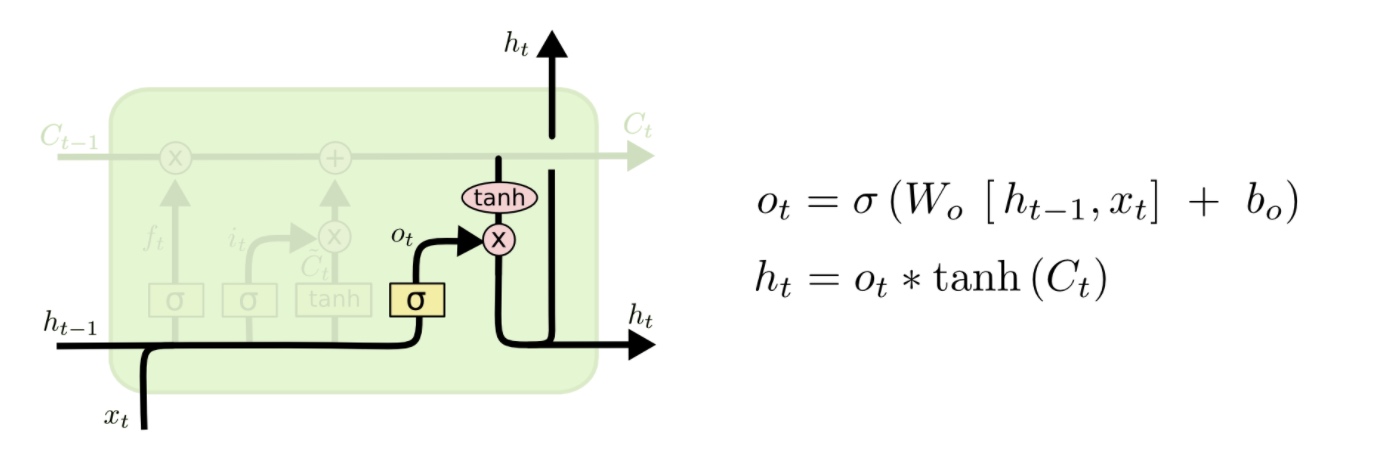
其中ht即是本层的输出,也是下一个单元的隐藏输入。
输入输出
# 输入
input = [seq_length, batch_size, input_size]
# 参数
weight = [num_directions, 4*hidden_size, input_size]
recurrence = [num_directions, 4*hidden_size, hidden_size]
bias = [num_directions, 8*hidden_size]
h0 = [num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size] #如果没有则全0
c0 = [num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size] #如果没有则全0
# 输出
output = [seq_length, num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size]
output_h = [num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size] #最后一个seq的输出
output_c = [num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size] #最后一个seq的输出
参考代码
onnx代码:
def step(self): # type: () -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]
seq_length = self.X.shape[0]
hidden_size = self.H_0.shape[-1]
batch_size = self.X.shape[1]
Y = np.empty([seq_length, self.num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size])
h_list = []
[p_i, p_o, p_f] = np.split(self.P, 3)
H_t = self.H_0
C_t = self.C_0
for x in np.split(self.X, self.X.shape[0], axis=0):
gates = np.dot(x, np.transpose(self.W)) + np.dot(H_t, np.transpose(self.R)) + np.add(
*np.split(self.B, 2))
i, o, f, c = np.split(gates, 4, -1)
i = self.f(i + p_i * C_t)
f = self.f(f + p_f * C_t)
c = self.g(c)
C = f * C_t + i * c
o = self.f(o + p_o * C)
H = o * self.h(C)
h_list.append(H)
H_t = H
C_t = C
concatenated = np.concatenate(h_list)
if self.num_directions == 1:
Y[:, 0, :, :] = concatenated
if self.LAYOUT == 0:
Y_h = Y[-1]
else:
Y = np.transpose(Y, [2, 0, 1, 3])
Y_h = Y[:, :, -1, :]
return Y, Y_h
由于LSTM参数很多,训练难度大,通常会使用参数更少的GRU。
GRU
GRU:Gated Recurrent Unit,门控循环单元,是LSTM的变体。循环过程中仅一个隐藏输入往后传递。原理如下图:
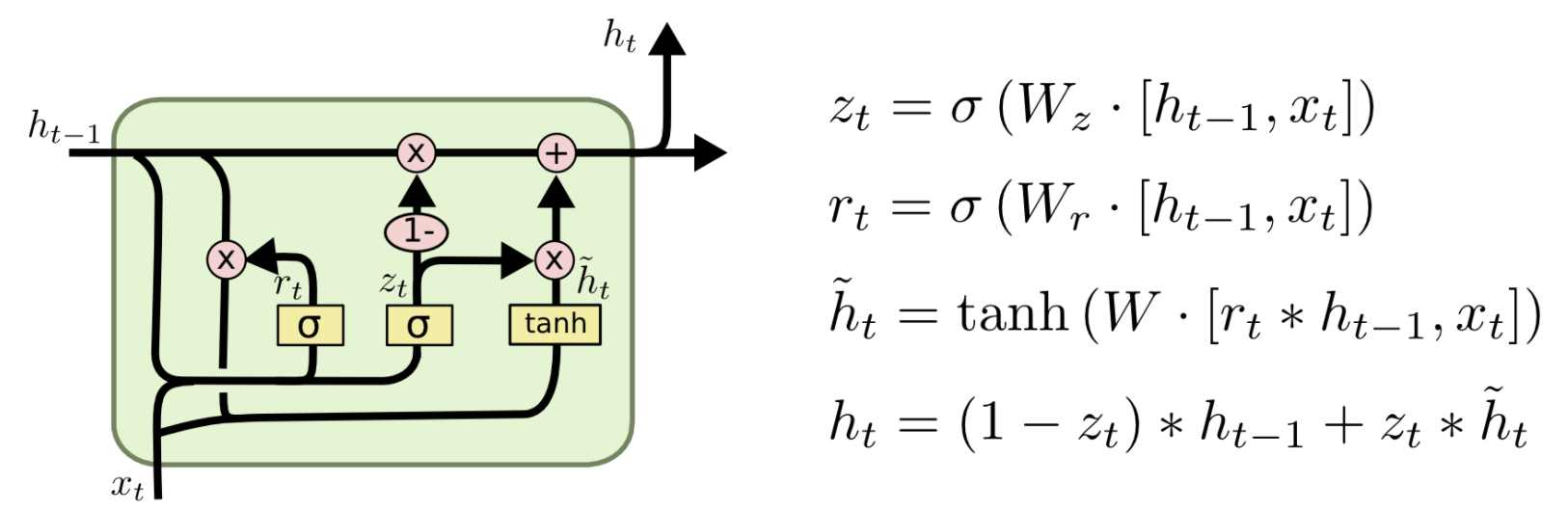
输入输出
# 输入
input = [seq_length, batch_size, input_size]
# 参数
h0 = [num_direction, batch_size, hidden_size]
weight = [num_direction, 3 * hidden_size, input_size]
recurrence = [num_direction, 3 * hidden_size, hidden_size]
bias = [num_direction, 6 * hidden_size]
# 输出
output = [seq_len, num_direction, batch_size, hidden_size]
output_h = [num_direction, batch_size, hidden_size]
计算过程如下(pytorch与onnx最后一步与图中不同):
\[z_t = sigmoid(W_{iz}x_t + b_{iz} + W_{hz}h_{t-1} + b_{hz}) \\ r_t = sigmoid(W_{ir}x_t + b_{ir} + W_{hr}h_{t-1} + b_{hr}) \\ n_t = tanh(W_{in}x_t + b_{in} + W_{hn}h_{t-1} + b_{hn}) \\ h_t = (1 - z_t)*n_t + z_t * h_{t-1}\]参考代码
onnx代码实现如下:
def step(self): # type: () -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]
seq_length = self.X.shape[0]
hidden_size = self.H_0.shape[-1]
batch_size = self.X.shape[1]
Y = np.empty([seq_length, self.num_directions,
batch_size, hidden_size])
h_list = []
[w_z, w_r, w_h] = np.split(self.W, 3)
[r_z, r_r, r_h] = np.split(self.R, 3)
[w_bz, w_br, w_bh, r_bz, r_br, r_bh] = np.split(self.B, 6)
gates_w = np.transpose(np.concatenate((w_z, w_r)))
gates_r = np.transpose(np.concatenate((r_z, r_r)))
gates_b = np.add(np.concatenate((w_bz, w_br)),
np.concatenate((r_bz, r_br)))
H_t = self.H_0
for x in np.split(self.X, self.X.shape[0], axis=0):
gates = np.dot(x, gates_w) + np.dot(H_t, gates_r) + gates_b
z, r = np.split(gates, 2, -1)
z = self.f(z)
r = self.f(r)
h_default = self.g(np.dot(x, np.transpose(w_h)) +
np.dot(r * H_t, np.transpose(r_h)) + w_bh + r_bh)
h_linear = self.g(np.dot(x, np.transpose(w_h)) +
r * (np.dot(H_t, np.transpose(r_h)) + r_bh) + w_bh)
h = h_linear if self.LBR else h_default
H = (1 - z) * h + z * H_t
h_list.append(H)
H_t = H
concatenated = np.concatenate(h_list)
Y[:, 0, :, :] = concatenated
if self.LAYOUT == 0:
Y_h = Y[-1]
else:
Y = np.transpose(Y, [2, 0, 1, 3])
Y_h = Y[:, :, -1, :]
return Y, Y_h
LSTM和GRU都可以支持双向,双向时输入先正向跑一个输出,再反向跑一个反向的输出,再结果合并。正向反向的输入是同一个,但参数是各自的参数。
